Analysis
Overview
In order that new project's persistence could be implemented, immutable structures are needed - like immutable tree. Immutability requires that every operation delivers reference to a new tree, in which changes (one defined by the operation) are made, in same time not modifying the tree of origin. In that sense, operation should use data of the origin tree as much as possible, and add/remove/change elements only where needed.
Working branch of the task is http://www.sophie2.org/trac/browser/branches/second_resource_refactoring
Task requirements
Following steps should be fulfilled:
- Tree/Map/Set Interface should be introduced
- Red-Black implementation of a tree (in order to get O(log n) worst case time complexity)
- Hashing class
Task result
Source code that contains working hierarchy of persistence structures with arbitrary hashing ability.
Implementation idea
Simple implementation hierarchy and name convention:
- Collection
- List
- Set
- Map
- Tree
- Hashing Tree
For the hashing purposes, several already existing classes are introduced (like Hash, Hasher...). Good idea for the names of the classes and methods is to add "imm" prefix to classes that contain structures and are used to store persistent data.
Related
(Add links to related tasks that could be useful or helpful.)
How to demo
Result of the time-capacity performance of the Red-Black tree.
Design
The working branch for the hierarchy of the classes:
- branch: http://www.sophie2.org/trac/browser/branches/second_resource_refactoring/ - second_resource_refactoring
- module: http://www.sophie2.org/trac/browser/branches/second_resource_refactoring/sophie2-platform/modules/org.sophie2.base.commons/src/main/java/org/sophie2/base/commons/structures?rev=5637 - org.sophie2.base.commons
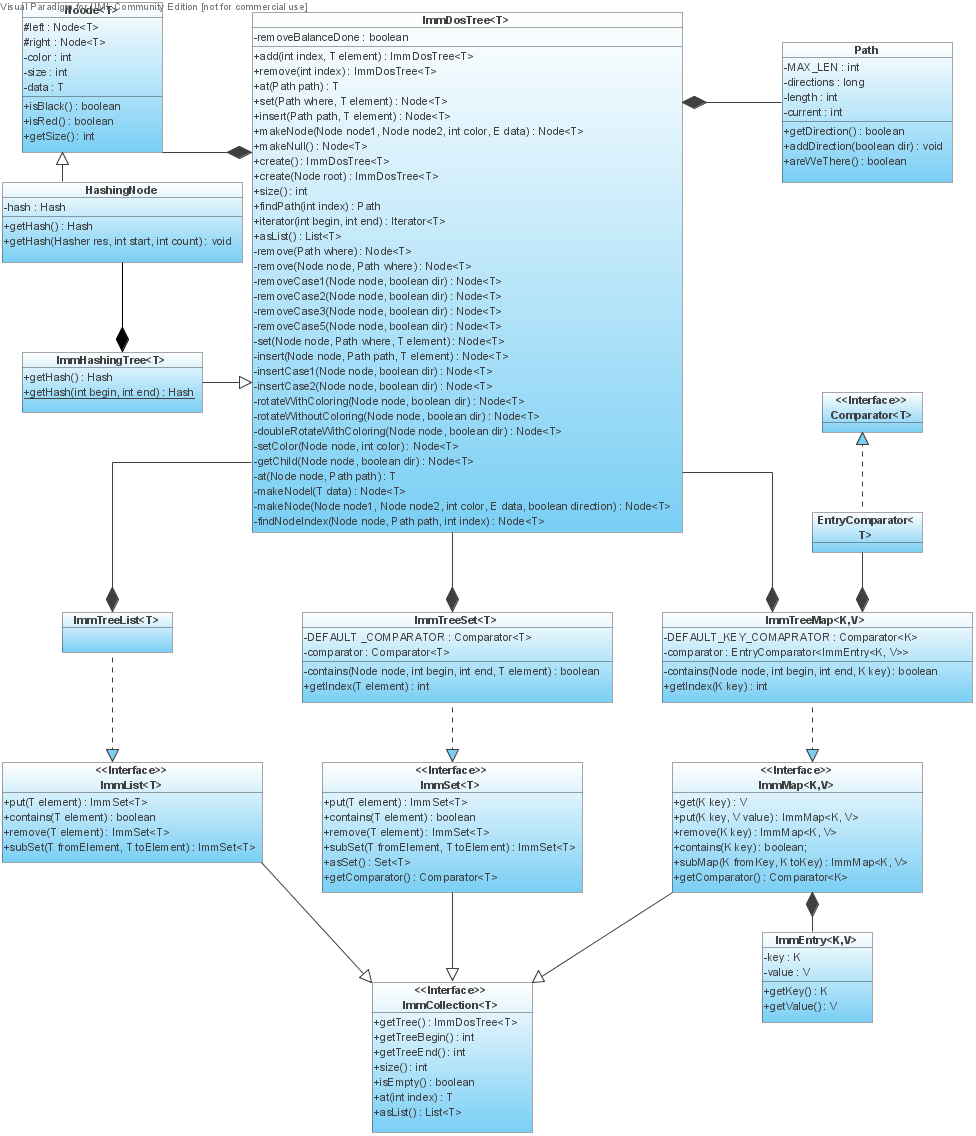
Class ImmDosTree will be the implementation of Red-Black indexed tree following methods will be introduced (only description in logical sense):
- add element - following methods are logical consequence of the add cases in the Red-Black tree algorithm.
- addCase1
- addCase2
- set element
- remove element - following methods are logical consequence of the remove cases in the Red-Black tree algorithm.
- removeCase1
- removeCase2
- removeCase3
- removeCase4
- removeCase5
- create - this method is used, when extending ImmDosTree class, to be overridden and to able to create an instance of the specific class, not its parent's class.
ImmDosTree's extension - ImmHashingTree contains hashable Nodes. ImmHashingTree contains static method getHash(...) with ImmCollection as argument, which in itself invokes a public method in the inner class HashingNode, for calculating the hash value needed:
public static Hash getHash(ImmCollection<?> col, int begin, int end) {
if(!(col instanceof ImmTreeCollection<?>)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non Hashable Collection - cannot get Hash!");
}
ImmTreeCollection<?> treeCol = (ImmTreeCollection<?>)col;
if(!(treeCol.getTree().getRoot() instanceof HashingNode<?>)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non Hashable Tree - cannot get Hash!");
}
HashingNode<?> node = (HashingNode<?>)treeCol.getTree().getRoot();
Hasher res = new Hasher();
int count = end - begin;
node.getHash(res, begin + treeCol.getTreeBegin(), count);
return res.toHash();
}
Following code (that is in HashingNode - the inner class in ImmHashingTree) realizes recursive calculation of the hash in limited sub-tree:
public void getHash(Hasher res, int start, int count) {
assert start >= 0;
assert count <= getSize();
int end = start + count;
if(start == 0 && count == getSize()) {
res.addHashed(getHash());
return;
} if (count == 0) {
return;
}
if(start < getLeft().getSize()) {
int leftStart = start;
int leftCount = Math.min(getLeft().getSize() - leftStart, count);
getLeft().getHash(res, leftStart, leftCount);
}
if(start <= getLeft().getSize() && end > getLeft().getSize()) {
res.addObject(getData());
}
if(end > getLeft().getSize() + 1) {
int rightStart = Math.max(0, start - getLeft().getSize() - 1);
int rightCount = (end - getLeft().getSize() - 1) - rightStart;
getRight().getHash(res, rightStart, rightCount);
}
}
Interfaces will be introduced in order to have uniform defined operations over the structures. A prototypes are as follows:
- List interface should be implemented for the ImmTreeList class. http://www.sophie2.org/trac/attachment/wiki/IMMUTABLE_TREE_R0/ImmList.java
- Set interface should be implemented for the ImmTreeSet class. http://www.sophie2.org/trac/attachment/wiki/IMMUTABLE_TREE_R0/ImmSet.java
- Map interface should be implemented for the ImmTreeMap class. http://www.sophie2.org/trac/attachment/wiki/IMMUTABLE_TREE_R0/ImmMap.java
Following UML class diagram describes the class hierarchy that should be implemented:
- Design related code:
- Tests:
Implementation
Added [5678] by the reviewer.
Testing
Comments
(Write comments for this or later revisions here.)
Attachments
- imm.png (111.8 KB) - added by stefan 16 years ago.
- ImmList.java (2.4 KB) - added by stefan 16 years ago.
- ImmSet.java (1.6 KB) - added by stefan 16 years ago.
- ImmMap.java (2.2 KB) - added by stefan 16 years ago.